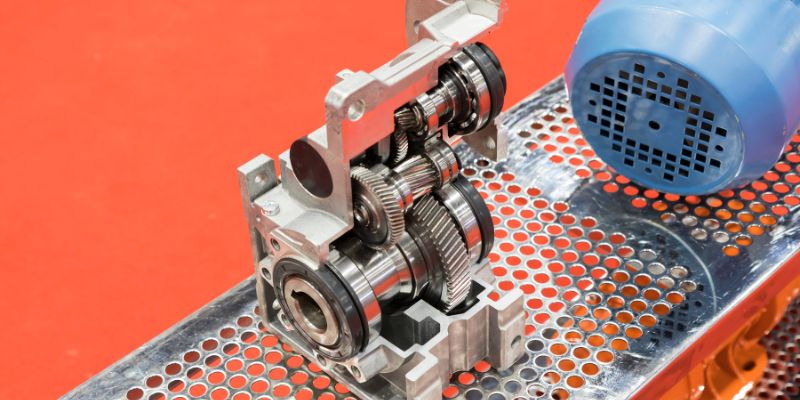
Gear pumps are used to move liquids or fluids from one place to another. There are three types of gear pumps: external gear pumps, internal gear pumps, and gerotor pumps. External gear pumps are used for industrial applications, internal gear pumps are used in more precise applications, and gerotor pumps are used for applications that need precise control of the flow rate.

Gear pumps are an essential part of many industrial operations, as they are capable of providing high pressure and efficient operation. Gear pumps are used in a wide range of applications, including oil and gas, chemical, and water processing. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the different types of gear pumps and their operation, components, maintenance, efficiency, variations, installation, benefits, and common applications. We’ll also provide troubleshooting tips for addressing any issues that may arise. By the end of this blog post, you will have a better understanding of how gear pumps work and the different types that are available.
Different Types of Gear Pumps
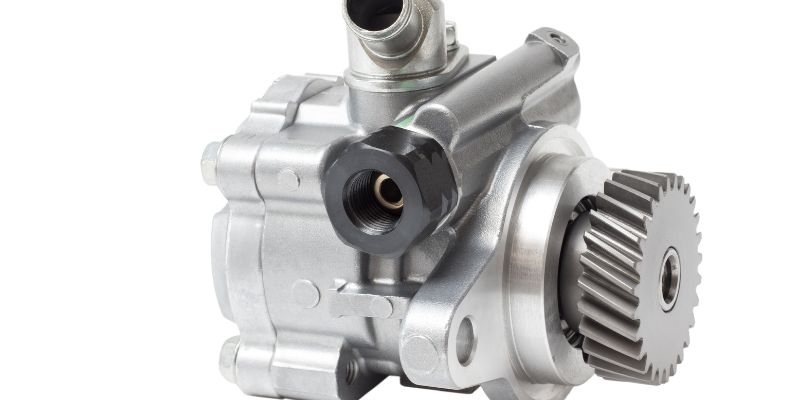
Gear pumps are versatile and powerful machines that are used in a wide variety of industries for a number of purposes. They operate by using two meshing gears to move fluid from one side of the pump to the other. The two most common types of gear pumps are external gear pumps and internal gear pumps. External gear pumps have two external gears that rotate in opposite directions, while internal gear pumps have an internal gear and an external gear that rotate in the same direction.
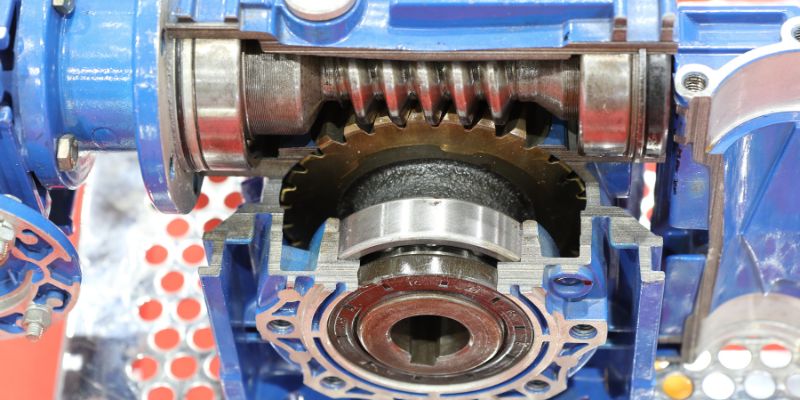

In addition to these two types of gear pumps, there is also a third type known as a circumferential piston pump. This type of pump uses a series of pistons that move in a circular pattern to move fluid from the inlet to the outlet. Unlike the other two types of gear pumps, circumferential piston pumps are not commonly used in industry, as they are more expensive and require more maintenance.
Regardless of the type of gear pump you choose, it is important to understand the benefits and drawbacks of each type before making a decision. External gear pumps are typically more affordable than internal gear pumps, while internal gear pumps are more efficient, reliable, and durable. Circumferential piston pumps, while more expensive, offer the advantage of being able to handle higher pressures and higher temperatures.
No matter what type of gear pump you are in the market for, it is important to do your research and understand the different types of gear pumps before making a purchase. Knowing the differences between external gear pumps, internal gear pumps, and circumferential piston pumps will help you make an informed decision and ensure you get the best pump for your needs.
Gear Pump Operation
Gear pumps are an important part of many industrial and automotive applications, used to move fluids such as oils, fuels, and water. Understanding how gear pumps work and the roles of the various components can help you choose the right pump for your needs.
The basic design of a gear pump consists of two interlocking gears, usually with a drive shaft coming from an electric motor or other power source. The gears rotate in opposite directions, trapping and pushing fluid through the pump. The two gears are supported by bearings and housed in a casing, usually made of cast iron, aluminum, or other durable material.
The drive shaft is connected to the gears by a set of meshing gears or a belt drive. This connection allows the drive shaft to spin the gears, thus moving the fluid through the pump. The speed of the pump is determined by the speed of the drive shaft.
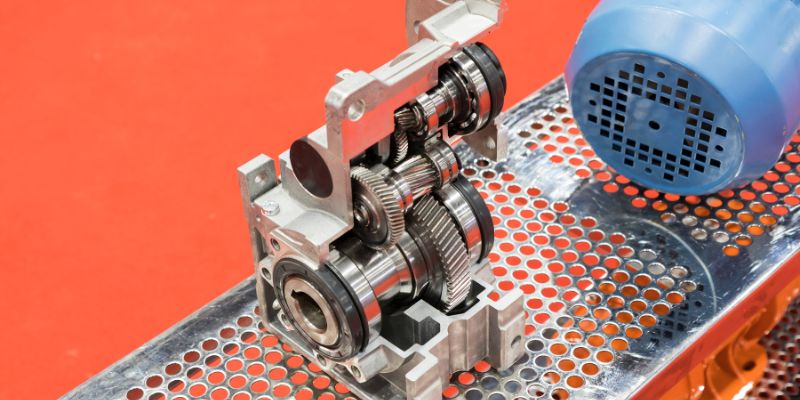
The casing also houses a relief valve, which helps regulate the pressure of the fluid as it passes through the pump. This valve is set to a predetermined pressure and will open if the pressure in the pump is too high.
The pump also contains a set of suction and discharge valves. These valves control the flow of fluid, and the size of the valves determines the flow rate of the pump. The suction valve is usually located at the entrance of the pump, while the discharge valve is located at the exit.
Finally, the pump needs to be sealed to prevent any leakage of the fluid. This is usually accomplished by using a set of gaskets or O-rings.
Understanding how gear pumps work and the roles of the various components can help you pick the right pump for your needs. Gear pumps are available in a variety of sizes, materials, and designs, making it easy to find one that will meet your requirements.
Gear Pump Components
Gear pumps are an essential component in many industries, providing precise and reliable pumping action for a variety of materials. But what are the components that make up a gear pump? Understanding the parts of a gear pump can help you to better maintain and troubleshoot your pump, while also providing insight into the types of pumps available on the market.
The basic components of a gear pump are the housing, the gears, and the drive shaft. The housing provides an enclosure for the gears and drive shaft, helping to protect them from external elements. Inside the housing, two interlocking gears spin in opposite directions, creating a pumping action that moves the material through the pump. The drive shaft connects the pump to the motor, allowing it to be powered and run.
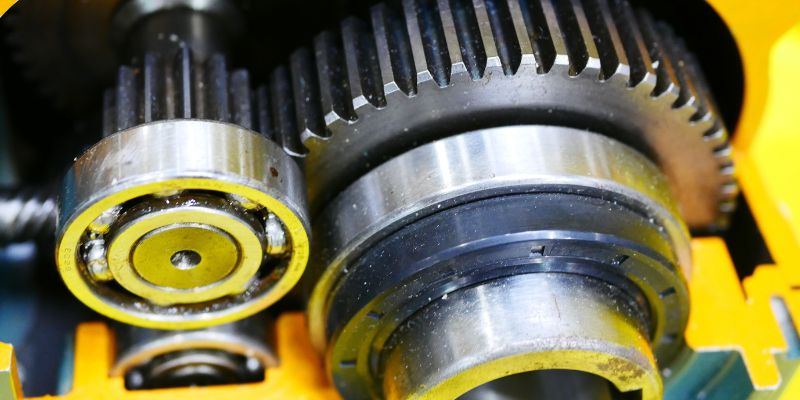

In addition to the basic components, there are also various other components that make up a gear pump. These components include the bearing, shaft seal, suction and delivery valves, and the hydraulic circuit. The bearings provide support for the drive shaft and allow it to rotate freely. The shaft seal keeps the lubricant inside the pump, while the suction and delivery valves regulate the flow of material. Lastly, the hydraulic circuit helps to control the pump’s speed and pressure.
When it comes to selecting a gear pump, it’s important to consider the type of material you’ll be pumping, as well as the flow rate and pressure requirements. Gear pumps come in a variety of sizes and configurations, and the right pump for your application will depend on the specific requirements. Knowing the components that make up a gear pump can help you to make an informed decision when selecting the best pump for your needs.
Gear Pump Maintenance
Proper maintenance of gear pumps is essential to ensure they function reliably and efficiently. Gear pumps are made up of two intermeshing gears that rotate and create a vacuum that draws liquid in and pumps it out. This type of pump is used in a variety of industrial applications, such as hydraulic systems, fuel transfer and chemical processing.
To keep gear pumps functioning properly, it is important to follow a regular maintenance schedule. Here are some common maintenance steps and tips to help keep gear pumps running smoothly:
1. Clean the filter screen: It is important to periodically clean the filter screen on the gear pump to remove any debris or contaminants that may have built up. This will help ensure that the pump is able to draw in the liquid without obstruction.
2. Lubricate the gears: Gear pumps require regular lubrication to ensure smooth operation. Use a quality lubricant designed for gear pumps and make sure to check the lubrication level at regular intervals.
3.Check for wear and tear: Regularly inspect the gears for signs of wear and tear. If any parts are worn or damaged, they should be replaced as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
4. Check the pressure: Make sure to check the pressure of the gear pump regularly to make sure it is within the manufacturer’s recommended range. Low or high pressure can cause the pump to malfunction.
5. Check the seals: The seals on the gear pump should be checked regularly to make sure they are intact and free of damage.
By following these simple maintenance steps, you can help ensure that your gear pump remains in good working condition and continues to work reliably. If you have any questions or concerns about the maintenance of your gear pump, contact your local pump specialist for advice and assistance.
Gear Pump Efficiency
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High efficiency | Expensive to maintain |
| Durable | Limited flow capacity |
| Easy to maintain | High speed operation can be noisy |
| Low vibration | Expensive to install |
| Low maintenance costs | Low operating pressure |
Gear pumps are one of the most efficient and cost-effective ways to move fluids. They are used in a variety of applications, from industrial to automotive to medical. However, there are both advantages and disadvantages to using a gear pump. The table above outlines the pros and cons of gear pump efficiency.
When looking at the advantages of using a gear pump, it is clear to see that they are highly efficient, durable, and easy to maintain. They also have low vibration, which can help reduce noise levels. Furthermore, they are relatively inexpensive to install and maintain.
On the other hand, the disadvantages of using a gear pump include a limited flow capacity, high speed operation that can be noisy, and a low operating pressure. Additionally, they can be expensive to maintain over time.
Overall, it is important to weigh the pros and cons of gear pump efficiency in order to determine if it is the right solution for your needs. With the right knowledge and research, you can make an informed decision that will best suit your needs.
Gear Pump Variations
When it comes to pumping liquids, gear pumps are one of the most popular and versatile solutions available. Gear pumps come in a variety of types and sizes, allowing them to be used for a wide range of applications. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of gear pumps and their various uses.
External Gear Pumps are the most common type of gear pump, and they are used in many industrial applications, including oil and fuel transfer, chemical processing and hydraulic systems. External gear pumps use two meshing gears to create suction and pressure, which forces the liquid through the pump. These pumps are typically simple in design and low in cost, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Internal Gear Pumps are similar to external gear pumps, but they use an internal gear instead of an external gear. This type of pump is often used in applications that require high pressures and high efficiency. The internal gear creates a vacuum, which allows the pump to maintain a constant flow rate.
Helical Gear Pumps are also known as helical lobe pumps, and they are typically used for higher-pressure applications. The pump is made up of two interlocking helical gears, which creates a pressure differential that pushes the liquid through the pump. Helical gear pumps are capable of producing higher pressures than external or internal gear pumps, making them ideal for applications that require higher pressures.
Vane Pumps are another type of gear pump, and they are often used in applications that require high flow rates and pressures. Vane pumps use a rotating vanes to create suction, which forces the liquid through the pump. Vane pumps are typically more expensive than other types of gear pumps, but they are capable of producing higher pressures and flow rates.
As you can see, there are many different types of gear pumps available for a variety of applications. Each type of pump has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to consider the type of application when deciding on the best pump for your needs. No matter what type of pump you choose, you can be sure that it will be reliable and efficient.
Gear Pump Installation
Gear pumps are an efficient and reliable way to move liquids or gases from one place to another. However, just like any other type of machinery, proper installation and maintenance are paramount to ensure effective and safe operation.
When installing a gear pump, it’s important to consider the type of pump that best fits your needs. There are two main types of gear pumps: external and internal gear pumps. External gear pumps are known for their simple design, high efficiency and low cost. They are often used in commercial applications, such as agricultural irrigation or in manufacturing operations. Internal gear pumps, on the other hand, are more complex and expensive. However, they are better suited for applications that require precise fluid control and higher pressures.
Once you’ve chosen the right type of gear pump, it’s important to take the necessary steps to ensure a proper installation. This includes choosing the right location, securely mounting the pump to the surface, and properly connecting all of the necessary piping and wiring. Additionally, it’s essential to check for any damage or leaks and make sure all of the mechanical seals are properly fitted.
After the installation is complete, it’s important to check the pump’s performance. This can be done by running the pump and monitoring the pressure, temperature, and flow rate. If any of these parameters are outside the normal range, it’s important to make any necessary adjustments. Finally, it’s important to regularly inspect the pump for signs of wear and tear, and to perform any necessary maintenance.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your gear pump is properly installed and running efficiently. Proper installation and maintenance are essential for extending the life of the pump and ensuring safe and reliable operation.
Benefits of Using Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are a type of rotary positive displacement pump which are used for transferring fluids in various industrial and automotive applications. They are highly efficient, reliable, and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for many applications. In this blog post, we will explore the types of gear pumps and the advantages of using them.
There are two main types of gear pumps: external gear pumps (EGPs) and internal gear pumps (IGPs). EGPs are made up of two spur gears that are designed to move fluid in one direction. They are simple, robust, and reliable, making them a great choice for many applications. IGPs, on the other hand, are made up of a single internal gear, which is surrounded by an outer gear. They are more efficient than EGPs, and they are able to move fluids in both directions.
One of the main benefits of using gear pumps is their high efficiency. They are able to move fluids with minimal losses, which means that energy costs are reduced significantly. Additionally, gear pumps are able to handle a wide range of viscosities, making them ideal for a variety of applications. They can also be used for pumping highly viscous fluids, such as oils and lubricants.
Another advantage of using gear pumps is their maintenance-free operation. Because of their simple design, they require minimal maintenance, which helps to reduce operational costs. Additionally, they are able to operate quietly and without vibration, making them suitable for use in areas where noise levels need to be kept to a minimum.
Finally, gear pumps are highly cost-effective, making them an attractive option for many applications. They are easy to install and operate, and they require minimal maintenance, which helps to reduce operational costs.
In conclusion, gear pumps offer a number of advantages, such as high efficiency, low noise levels, minimal maintenance, and cost-effectiveness. They are a great choice for many industrial and automotive applications, and they offer a reliable and cost-effective way to move fluids.
Common Applications of Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are widely used in a variety of industries and applications. They are known for their reliable performance, easy maintenance and versatility. Gear pumps are used to move fluids at a controlled rate and are ideal for applications that require precision and/or high-pressure. Common applications of gear pumps include hydraulic systems, lubrication systems, fuel pumps, and cooling systems.
In hydraulic systems, gear pumps are used to deliver fluids at a constant rate and pressure. This type of pump is often used in industrial machinery, construction equipment and automobiles to manage the flow of oil, fuel, and other fluids. Gear pumps are also used in lubrication systems to deliver lubricating oil to bearings, gears and other components.
Fuel pumps, such as those found in automobiles, are often powered by gear pumps. The gear pump is used to transfer fuel from the tank to the engine and provide it at a constant pressure. Gear pumps are also used in cooling systems, such as those found in water heaters, to circulate coolant and regulate the temperature.
Gear pumps are also used in specialized applications, such as those found in medical equipment, food processing and pharmaceuticals. In medical equipment, gear pumps are used to deliver drugs and other substances at a precise rate. In food processing, gear pumps are often used to move viscous and sticky substances such as chocolate and icing. Gear pumps are also used in pharmaceuticals for transferring and measuring different types of liquids.
Overall, gear pumps are a reliable and versatile solution for a variety of applications. They are cost-effective, easy to maintain and provide consistent performance. With the wide range of applications, gear pumps are a popular choice for many industries.
Troubleshooting Gear Pump Issues
Troubleshooting gear pump issues can be a tricky process. Gear pumps are an important part of many systems, and when they malfunction, it can have serious consequences. Fortunately, there are some common issues that can crop up with gear pumps and knowing how to address them can help avoid major disruptions.
Gear pumps are divided into two types: internal and external. Internal gear pumps have an internal gear that rotates within an outer shell and is connected to a drive shaft. External gear pumps have an external gear that meshes with an internal gear. Each type of gear pump presents its own unique set of problems and requires a different approach to troubleshooting.
One of the most common issues with gear pumps is air entrapment. This occurs when air bubbles become trapped between the gears, which can cause cavitation and reduce the amount of liquid being pumped. To fix this, you should check the valve and relief settings. If the settings are too low, it can cause air to become trapped. Increasing the valve and relief settings and using an air-leak detector can help identify if air is being trapped in the pump.
Another common issue is wear and tear on the pump. Over time, the gears can become worn down and can cause the pump to lose efficiency. To address this problem, you should check the lubrication levels and replace any worn components. Additionally, you should regularly inspect the pump for signs of wear and tear and replace any parts that are showing signs of wear.
Finally, clogging can be a major issue with gear pumps. Clogs can occur when a foreign object, such as a piece of debris, gets stuck in the pump. To prevent this, you should regularly inspect the pump for signs of clogs and use a filter to keep debris out of the system. Additionally, you should check the valves and suction lines for blockages and remove them if necessary.
By understanding common issues with gear pumps and how to address them, you can help prevent major disruptions in your system. Regularly inspecting the pump, checking the settings and valves, and replacing worn components can help keep your gear pump in top shape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gear pumps are a versatile and efficient type of pump that can be used in a variety of applications. There are several types of gear pumps available, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. Knowing the different types of gear pumps, how they work, and the maintenance requirements is key to ensuring the pumps operate efficiently and reliably. With proper installation and maintenance, gear pumps can provide users with reliable performance for many years.
Related Post: