A rotor is an important part of a pump. It is a round metal piece that spins and helps push liquids or other substances through the pump. It is connected to an electric motor which helps it spin. Without a rotor, the pump wouldn’t be able to do its job.
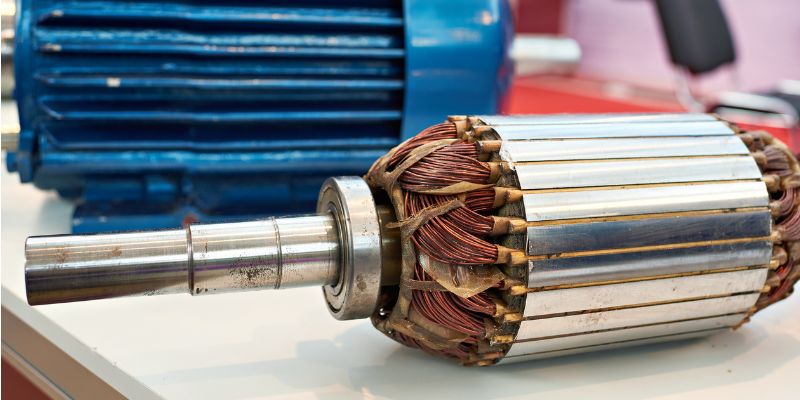
A rotor in a pump is a rotating component that is used to help move liquids or gases. It is typically made from metal and has a variety of blades or vanes that help to create a vacuum or pressure to push the fluid through the pump. The rotor can be made from different materials and can be designed in a variety of shapes and sizes to fit the specific needs of the pump. In this blog post, we will discuss the definition of a rotor in a pump, the types of rotors, their advantages and disadvantages, common applications, and maintenance and troubleshooting tips. We will also compare different types of rotors in a pump.
Types of Rotors in a Pump
To better understand the components of a pump, it is important to recognize the manufacturing process and different designs of rotors in a pump.
Manufacturing Process for Rotors in a Pump
A rotor is a key component of a pump and is responsible for powering the mechanical motion of the pump. In order for a pump to function, the rotor must be manufactured in a specific manner to ensure it is durable and reliable. The manufacturing process for rotors in a pump typically involves the following steps:
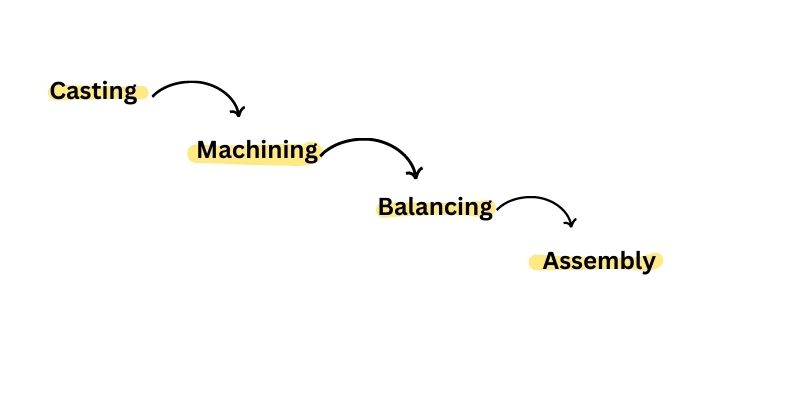
1. Casting: This is the process of pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify. This is done to make sure the rotor has the desired shape and dimensions.
2. Machining: After the rotor has cooled and solidified, it is machined to create the desired finish and ensure the rotor is to the required specifications.
3. Balancing: Once the rotor has been machined, it is balanced to ensure its performance is as expected. This is done by measuring the mass distribution of the rotor and then adding or removing material to offset any imbalances.
4. Assembly: The rotor is then assembled with other components such as bearings and seals to ensure it is ready to be used in the pump.
By following these steps, manufacturers can ensure that their rotors are manufactured to the highest quality and are reliable and durable. Understanding the manufacturing process for rotors in a pump is essential for ensuring your pump will perform as expected.
Different Designs of Rotors in a Pump
When it comes to pumps, rotors play an important role in their operation. A rotor is essentially a rotating component, usually a shaft, that helps to move liquids or gases through the pump as it rotates. Different designs of rotors in a pump can affect the performance of the pump, so it is important to understand the different types of rotors available.
One of the most common designs of rotors in a pump is the impeller rotor. This rotor is typically shaped like a propeller and has blades that spin inside a stationary housing. This type of rotor is used to create a vacuum or pressure in the pump to help move the liquid or gas.
Another type of rotor is the eccentric rotor. This type of rotor is a shaft that has an off-center weight attached to it. As the shaft rotates, the weight creates an eccentric motion that helps to move the liquid or gas through the pump.
The third type of rotor is the double-ended rotor. This rotor is essentially two rotors in one, with both ends spinning in opposite directions. The double-ended rotor helps to create more efficient pumping as it can draw in liquid or gas from both sides of the pump.
Finally, there is the axial rotor. This type of rotor is essentially a shaft with blades attached to it that spin along the length of the shaft. This type of rotor helps to create a steady flow of liquid or gas through the pump.
Understanding the different designs of rotors in a pump can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right pump for your application. With the right rotor design, you can ensure your pump operates efficiently and reliably.
Advantages of Using a Rotor in a Pump
Using a rotor in a pump is a great way to increase efficiency and longevity. A rotor is a rotating part of a pump, typically made from a shaft, that helps to move fluids or liquids through the pump. By utilizing a rotor, the pump can be designed to achieve greater pressure, flow rate, and power. This can result in increased levels of performance, as well as improved energy efficiency.
The advantages of using a rotor in a pump are numerous. First and foremost, it increases the efficiency of the pump by increasing the pressure, flow rate, and power of the pump, resulting in improved performance. Additionally, by using a rotor, the pump is able to operate with lower levels of vibration, which can reduce noise and wear. This can help to extend the life of the pump, as well as reduce maintenance costs.
The rotor also helps to keep the liquid or fluid moving in the right direction. This ensures that the fluid is not wasted, and that the pump is able to work as efficiently as possible. Additionally, the rotor can be used to create a backflow valve, which helps to reduce the risk of overpressurization and backflow.
Finally, using a rotor in a pump can help to improve the overall safety of the system. By reducing the vibration and noise of the pump, it can help to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, the backflow valve created by the rotor can help to protect the pump from overpressurization.
Overall, using a rotor in a pump can provide numerous benefits, from improved performance to increased safety. For these reasons, it is an excellent choice for any pump system.
Disadvantages of Using a Rotor in a Pump
Having a rotor in a pump can be a great asset for many applications, allowing for more precise control over the flow of liquids and solids. However, there are some potential drawbacks to using a rotor in a pump as well. Here, we’ll discuss some of the potential disadvantages of using a rotor in a pump.
The first disadvantage of using a rotor in a pump is the complexity of the system. Rotor pumps require complex components to operate, including drive shafts, bearings, seals, and more. As a result, they tend to be much more expensive to repair and maintain than other types of pumps. Additionally, they can be difficult to install and require a higher level of skill than other pumps.
Another disadvantage of using a rotor in a pump is that they are not always suitable for certain applications. For example, they are not suitable for use in highly abrasive fluids, as the rotor can be damaged by the abrasive particles. Additionally, they are not suitable for large-scale applications, as the rotor can cause cavitation when pumping at high flow rates.
Finally, rotor pumps are not as efficient as other types of pumps, as the rotor can cause increased turbulence and drag. This can lead to lower flow rates and increased energy consumption, resulting in higher operational costs.
Overall, rotor pumps can be great tools for many applications, but there are some potential drawbacks to using them. When deciding whether to use a rotor pump, it is important to weigh the pros and cons to ensure that the rotor is the best choice for the application.
Common Applications for Rotors in a Pump
Rotors are an integral part of pumps, as they help to move fluids or liquids through the pump. Rotors have the ability to rotate and generate a centrifugal force, which helps to create a pressure differential between the inlet and the outlet of the pump. This pressure differential is what propels the fluid or liquid through the pump.
In terms of pump applications, rotors are used in many different types of pumps, including centrifugal pumps, rotary pumps, and positive displacement pumps. Generally, rotors are used to create a pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the pump, which helps to move the fluid or liquid through the pump.
In terms of centrifugal pumps, rotors are used to force the fluid or liquid around the impeller. This creates a centrifugal force, which is used to generate the pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet of the pump. In rotary pumps, rotors are used to move the fluid or liquid through the pump by using a rotating motion. Positive displacement pumps also use rotors to generate a pressure differential between the inlet and the outlet of the pump, although these pumps use a different type of rotor than centrifugal and rotary pumps.
Rotors can also be used in chemical pumps to help move hazardous materials such as acids and alkalis. These pumps are often sealed to prevent any leakage of the hazardous material, and rotors are used to help generate the pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet.
Rotors can also be used in other types of pumps, such as vacuum pumps, hydraulic pumps, and even turbine pumps. In all cases, rotors are used to generate a pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet of the pump, which helps to move the fluid or liquid through the pump.
In conclusion, rotors are an essential part of many pumps, as they help to generate the pressure differential between the inlet and the outlet of the pump in order to move the fluid or liquid through the pump. Rotors are used in centrifugal pumps, rotary pumps, and positive displacement pumps, as well as in chemical, vacuum, hydraulic, and turbine pumps.
Maintenance for a Rotor in a Pump
In order to maintain a rotor in a pump and ensure its safe operation, it is important to understand the potential issues that can arise and how to safely handle them.
Troubleshooting Issues with Rotors in a Pump
Troubleshooting issues with rotors in a pump can be a daunting task, but with the right knowledge and a few helpful tips, you can have your pump running smoothly in no time. In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of a rotor in a pump and explore the common issues that can arise, as well as how to identify and address them.
As a first step, it’s important to understand the basics of a rotor in a pump. A rotor is a central rotating part of a centrifugal pump, which helps move liquid (or gas) through the pump. The rotor is typically made up of a series of blades that are designed to move material through the pump at a specific rate, depending on the speed of the rotor.
While rotors are designed to last, they can experience wear and tear over time, leading to issues such as decreased efficiency, increased noise, and even complete failure. It’s important to regularly inspect your rotor for signs of damage and wear, such as uneven blades, bent or broken blades, or signs of corrosion. It’s also important to ensure that the rotor is properly lubricated, as this can help reduce friction and wear.
If your rotor has experienced significant wear or damage, you’ll need to replace it. Fortunately, this is a relatively simple process that involves removing the old rotor and installing a new one. However, it’s important to make sure that the new rotor is compatible with your pump, as incompatible rotors can cause additional issues.
If your rotor is working properly, but you’re still experiencing issues with your pump, then it’s likely that something else is at fault. Common issues include clogged filters, blocked intake ports, and broken impellers. In order to identify and address these issues, it’s important to inspect the entire pump and all its components.
If you’re having trouble troubleshooting issues with your rotor in a pump, don’t hesitate to consult a professional. They’ll be able to advise you on the best course of action, as well as provide tips and advice to help keep your pump running smoothly.
By understanding the basics of a rotor in a pump and troubleshooting potential issues, you can ensure that your pump remains in top condition. With the right knowledge and a few helpful tips, you can have your pump running smoothly in no time.
Safety Considerations for Rotors in a Pump
When it comes to maintenance for a rotor in a pump, safety considerations must always be taken into account. Rotors in a pump are essential components of the system, and the consequences of failure can be catastrophic. To ensure the safety of a rotor in a pump, it is important to regularly inspect the rotor and its components, as well as any related safety systems. In addition, it is also important to regularly test the rotor for any signs of wear or damage.
When inspecting a rotor in a pump, it is important to look for any signs of corrosion, wear, or damage. Additionally, any loose or missing components should be replaced or repaired as soon as possible. Any components that are showing signs of wear should be replaced or repaired as well.
When testing a rotor in a pump, it is important to check the rotor’s performance. This includes checking the speed and torque of the rotor, as well as any other performance parameters. Additionally, any safety systems related to the rotor should also be tested. This includes any emergency shut-off systems or other safety systems.
It is also important to ensure that the rotor is properly lubricated. This includes regularly checking the oil level and the condition of the oil. If the oil is not in good condition, it should be replaced as soon as possible. Additionally, any lubrication points should be regularly checked for any signs of wear or leakage.
Finally, any components related to the rotor should also be regularly inspected and replaced if necessary. This includes any seals, gaskets, or other components that are showing signs of wear. Additionally, any components that are exposed to high temperatures should also be regularly inspected and replaced as necessary.
By following these safety considerations, you can ensure the safety of a rotor in a pump and its related components. Additionally, regular inspections and testing can help to identify any potential issues before they become a problem. By taking safety precautions, you can help to keep your pump running smoothly and safely.
Comparing Different Types of Rotors in a Pump
When it comes to pumps, the rotor is a key component. The rotor is the part of the pump that transfers energy from the motor to the fluid, allowing the pump to move the fluid through the system. Understanding the different types of rotors in a pump can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right pump for your needs.
When comparing different types of rotors in a pump, there are two main factors to consider: the number of stages and the size of the rotor. The number of stages refers to how much pressure is applied to the fluid by the rotor during the pumping process. The size of the rotor affects how much pressure can be applied to the fluid, and how much torque is required from the motor to turn the rotor.
Single-stage rotors typically have a larger diameter than multi-stage rotors, and can apply more pressure to the fluid. Multi-stage rotors, on the other hand, are made up of multiple discs or blades that rotate together, often at different speeds, to increase the pressure applied to the fluid. Although multi-stage rotors can create more pressure, they also require more torque from the motor, which can make them more expensive.
Another type of rotor is the helical rotor, which is made up of multiple blades arranged in a helical pattern. This type of rotor produces a slightly higher pressure than a single-stage rotor, and requires less torque from the motor. The helical rotor is often used in pumps that need to pump large volumes of fluids at high pressures, such as those used in water treatment plants.
Finally, there are also eccentric rotors, which are made up of two discs that rotate in opposite directions. This type of rotor is capable of producing high pressures, but also requires a large amount of torque from the motor.
Understanding the differences between the different types of rotors in a pump can help you make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the right pump for your needs. Consider your application, the amount of pressure needed, and the size of the rotor to ensure you make the best choice for your system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a rotor in a pump is a rotating mechanism that works with the motor to provide energy and pressure for pumping liquids. It comes in various designs, sizes and materials and has both advantages and disadvantages. The installation and maintenance of a rotor in a pump is important to ensure it works properly and safely in all applications. By comparing different types of rotors in a pump, one can choose the right one for their specific needs.
Related Post:
- What is an endo motor?
- What is gear ratio in endodontics?
- What is meant by 70% efficiency?
- What is rotary displacement pumps?
- What is rotary rct?